PHI CHINA Nanjing Laboratory Cooperation Achievements (1)
With rapid development in science and technology recent years, advanced surface analysis technology has become a necessary experimental technology for surface characteristics research in the fields of materials, energy, catalysis, microelectronics, and semiconductor industries.
XPS is an important scientific instrument in surface analysis, which can provide surface composition and chemical state information. It is widely used in scientific research and high-tech industries as well and take an important role to solve complex problems.
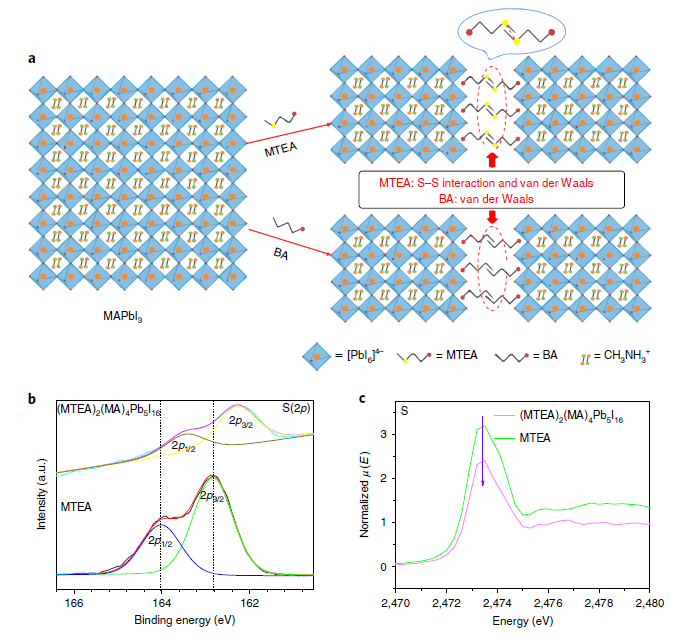
Perovskite materials itself have the characteristics of direct band gap, bipolar transport, high absorption coefficient, low exciton binding energy, long carrier diffusion distance and solvability. It has a rapid development in recent years. However, perovskite materials are sensitive under the effect of light, electric field, temperature, water and oxygen content in the environment, thus seriously hindering the commercialization of perovskite solar cells. Comparing to traditional three-dimensional (3D) halide perovskite solar cell materials, two-dimensional Ruddlesden–Popper (2DRP) layered perovskites exhibit improved photostability and thermal stability because of its’ improved moisture resistance, excellent light stability and thermal stability, ultra-low self doping behavior and significantly reduced ion migration effect. The stability of 2DRP layered perovskite come from the protection of organic amines on the surface, the effective regulation of perovskite tolerance factor in low dimension, and the interlayer interaction by the van der Waals force and hydrogen bond. But as the hydrogen bond and van der Waals force are weak, the improvement of the layered framework stability is limited, at the same time, the weak interaction between 2DRP perovskite layers limited it’s self-assembly and the charge transport across the layers. Therefore, the thin film quality of perovskite active layer and the separation and transmission characteristics of photocarriers are affected.
To solve this scientific quest, Huang Wei, academician of Flexible Electronics Research Institute, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Professor Chen Yonghua, Institute of advanced materials, Nanjing University of technology and Professor Zhang Lijun, National Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics / School of materials, Jilin University reported an efficient and stable layered perovskite solar cell together.
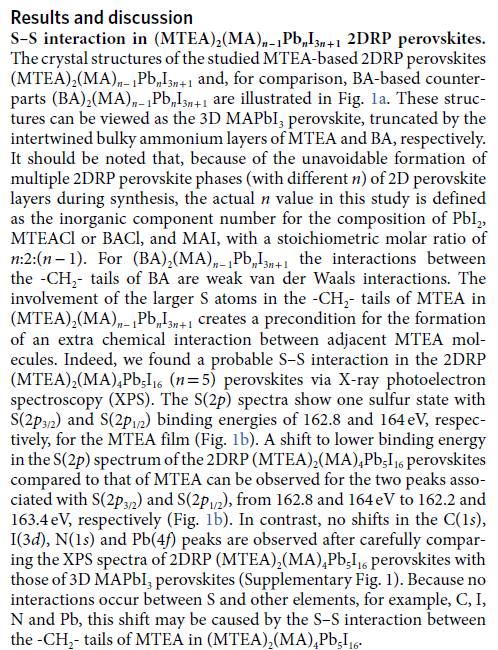
By innovatively introducing an organic amine with a S (Sulfur) atom, the interaction between the layers can be regulated effectively by the S-S interaction, the charge transfer across the layered are enhanced and the layered perovskite framework are further stabilized, and therefore prepared high performance 2DRP layered perovskite solar cells with efficiency reached 18.06% (certification efficiency 17.6%). Meanwhile, the reinforced interlayer interaction has significantly improved the moisture and thermal stability and the device stability of 2DRP perovskite film. The device can keep at maximum output under standard sun light for 1000 hours with less than 15% attenuation of efficiency. The related achievements were published in nature Photonics (nature photonics 14, 154 (2020). Doi: 10.1038 / s41566-019-0572-6) under the title of “Efficient and stable Ruddlesden–Popper perovskite solar cell with tailored interlayer molecular interaction”.
The mechanism of the interlayer interaction is one of the key points of this research. Dr. Ju Huanxin from Phi China Laboratory is honored to be in this research, measuring the XPS spectra of S2p, C1s, N1s, I3d and Pb4f through the high-resolution PHI XPS. The result of this research shown that the interaction of S elements provides a favorable data support for the study of kinetics, stability and charge transfer characteristics of 2DRP layered perovskite films.
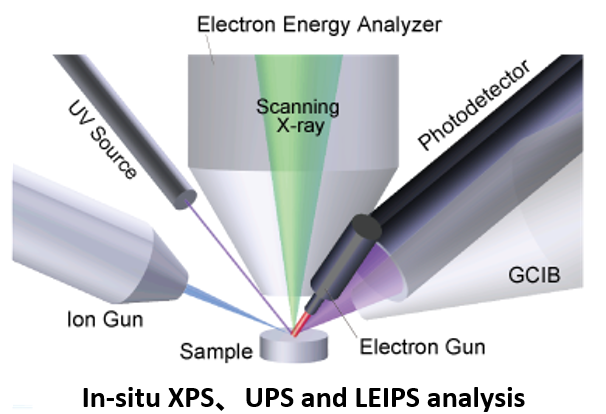
Introduction of PHI CHINA Nanjing Laboratory
PHI CHINA Nanjing laboratory was established in December, 2018. It is committed to provide technical support for PHI CHINA surface analysis equipment and promoting the application of advanced surface analysis technology in scientific research and high-tech industries through cooperation. At present, the XPS system in PHI CHINA laboratory integrates multiple surface analysis technologies (XPS-UPS-IPES-GCIB): the unique scanning-focus XPS can provide high surface sensitivity (
Dr. Ju Huanxin, former associate researcher at the National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory of the University of Science and Technology of China, is mainly engaged in the research of soft X-ray spectroscopy methodology and the electronic properties of energy materials / device interfaces. He joined PHI (China) Limited in November, 2018 as Application Scientist, responsible for the setup and operation management of PHI CHINA Nanjing surface analysis laboratory. In cooperation with users in academic research, he has published more than 80 academic papers in Nature Photonics, Nature Chemistry, Nature Energy, Nature communication, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, Adv. Mater and other journals.